「力扣」第 148 题:排序链表
传送门:148. 排序链表;
题解地址:自底向上的“归并排序”(Java 代码)。
在 $O(n log n)$ 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
示例 1:
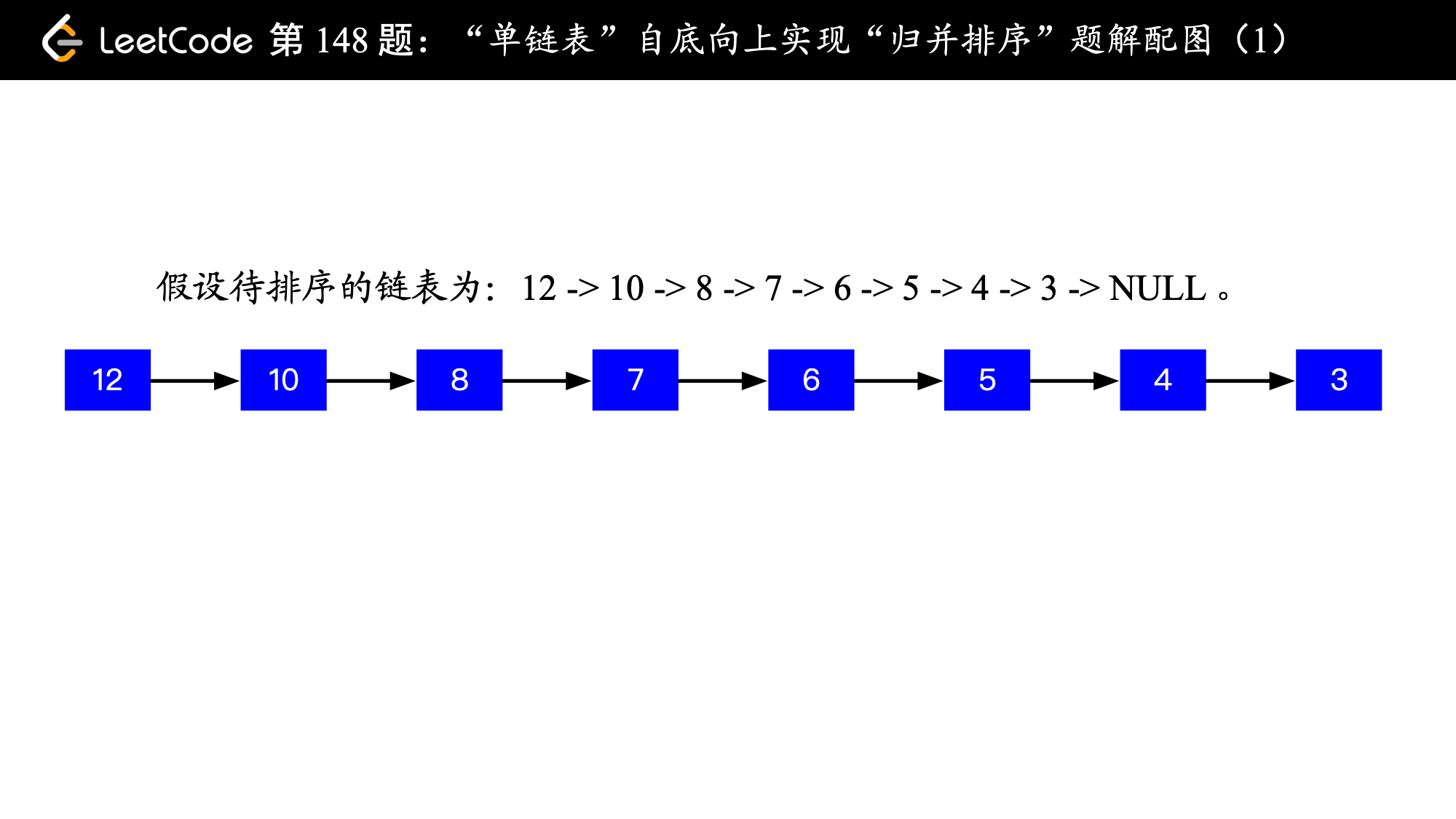
输入: 4->2->1->3
输出: 1->2->3->4
示例 2:输入: -1->5->3->4->0
输出: -1->0->3->4->5
自底向上的“归并排序”(Java 代码)
这个方法比较 tricky,可能编码上还有优化的空间,大家看一看就好了。
(温馨提示:下面的幻灯片中,有几页上有较多的文字,可能需要您停留一下,可以点击右下角的后退 “|◀” 或者前进 “▶|” 按钮控制幻灯片的播放。)
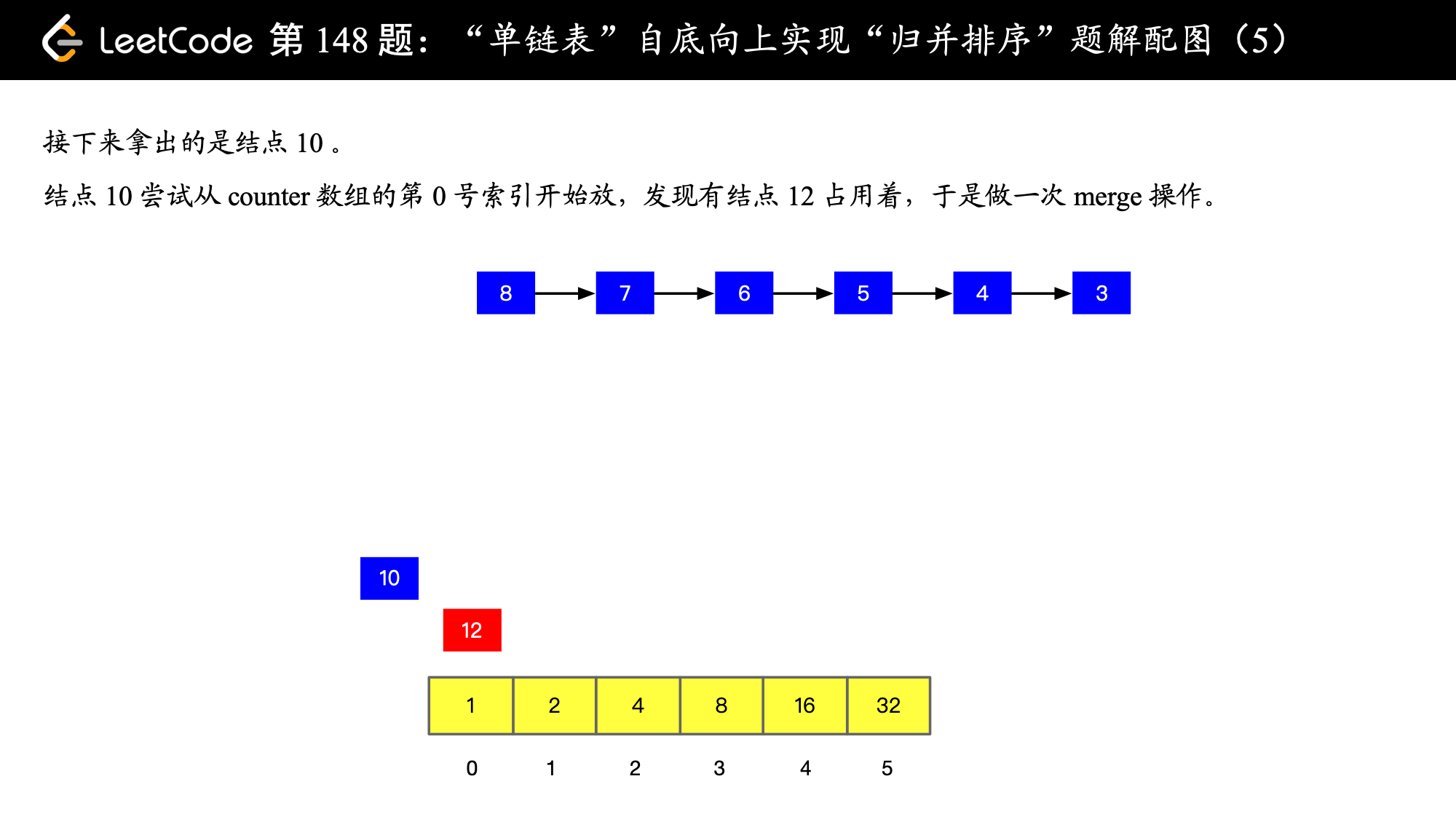
 ),
), ),
), ),
), ),
), ),
),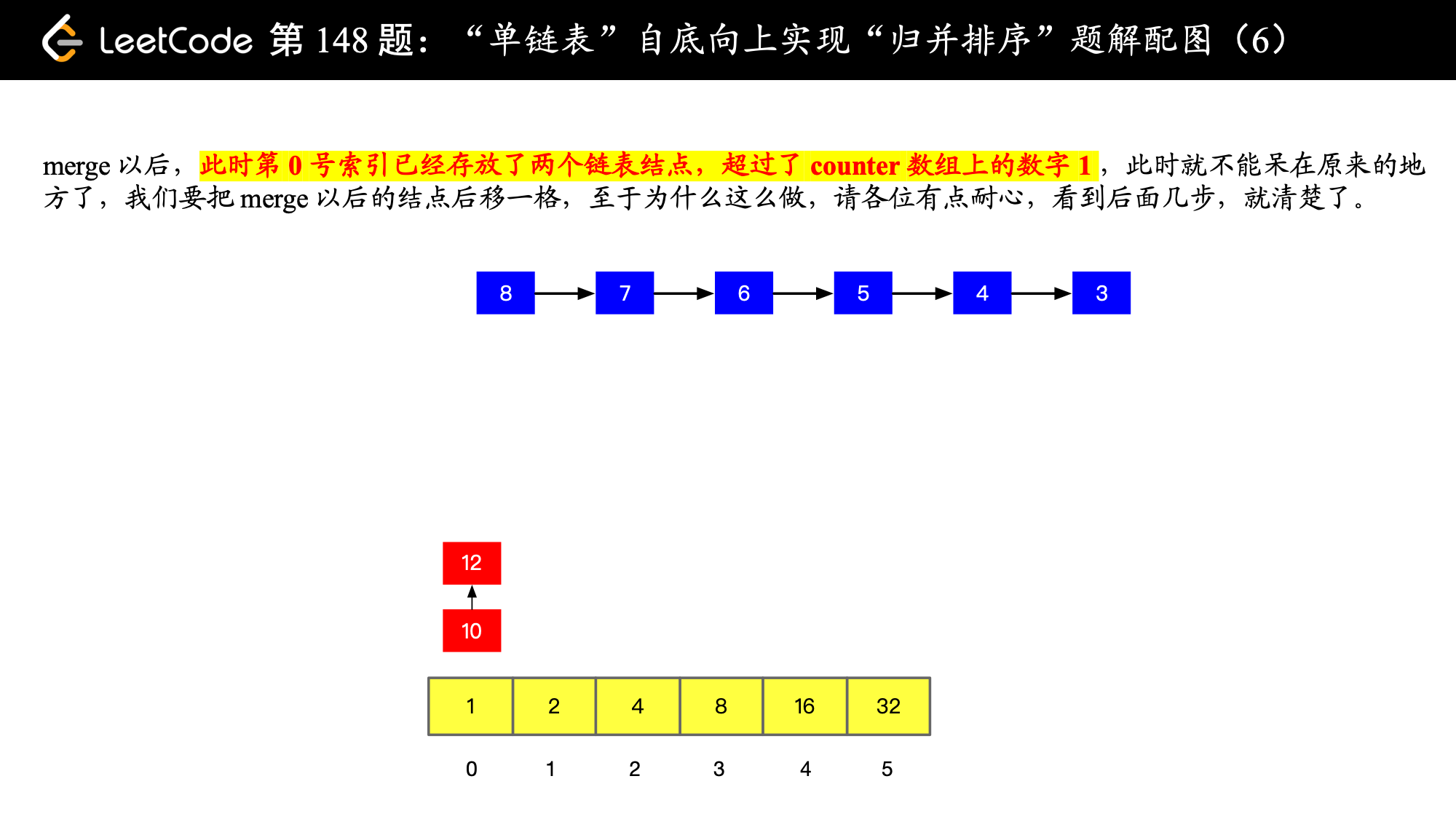 ),
),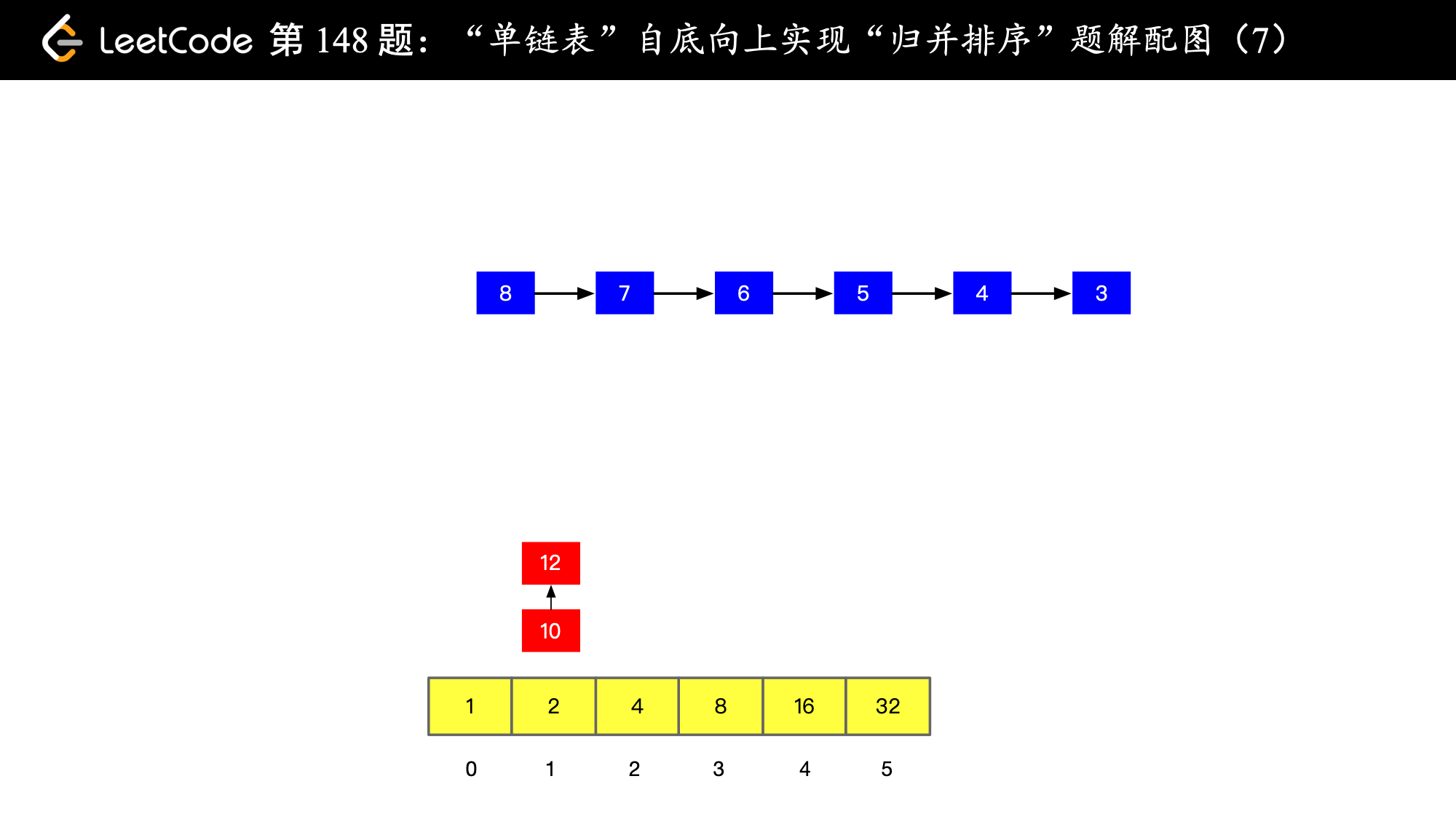 ),
),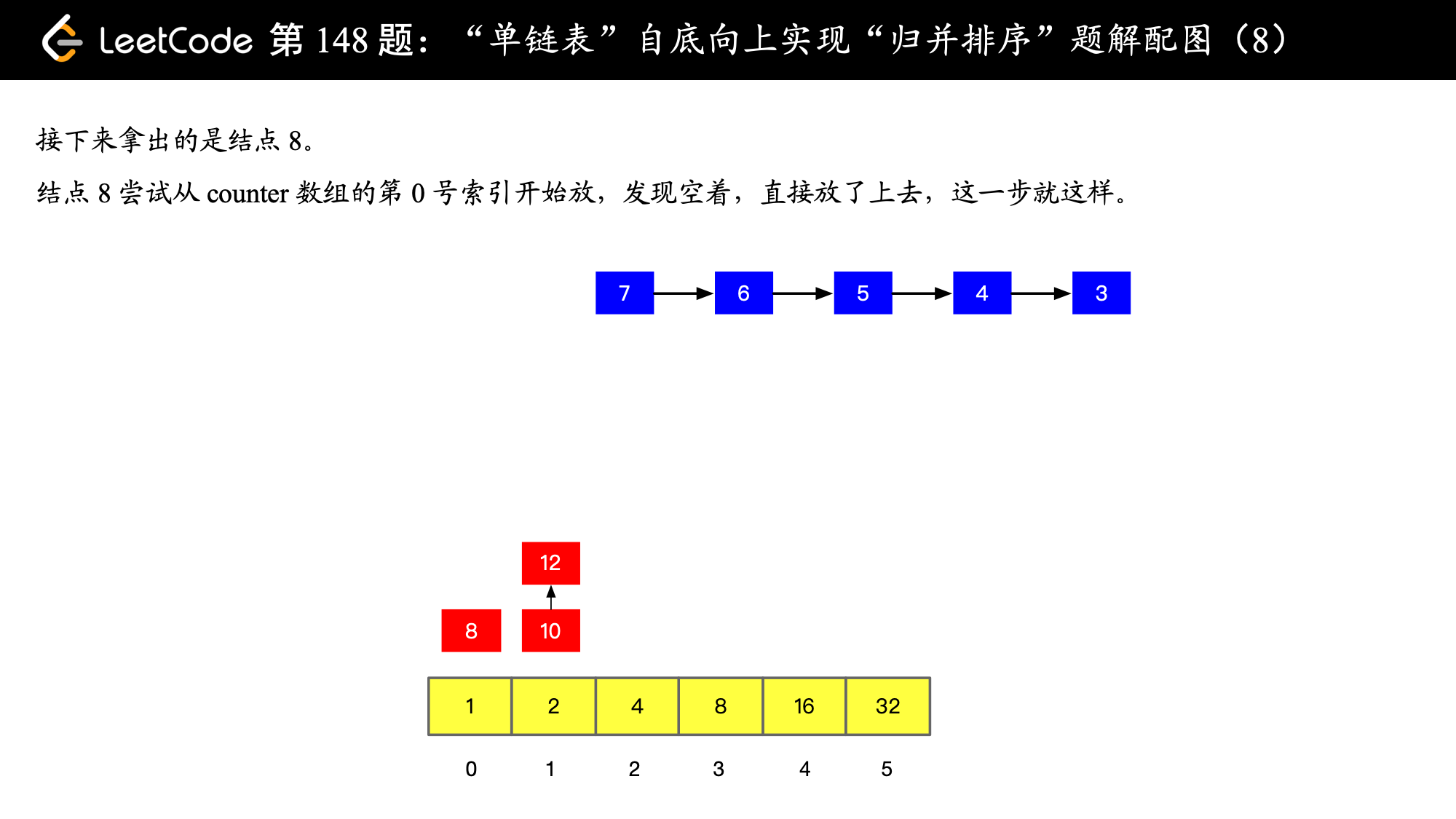 ),
),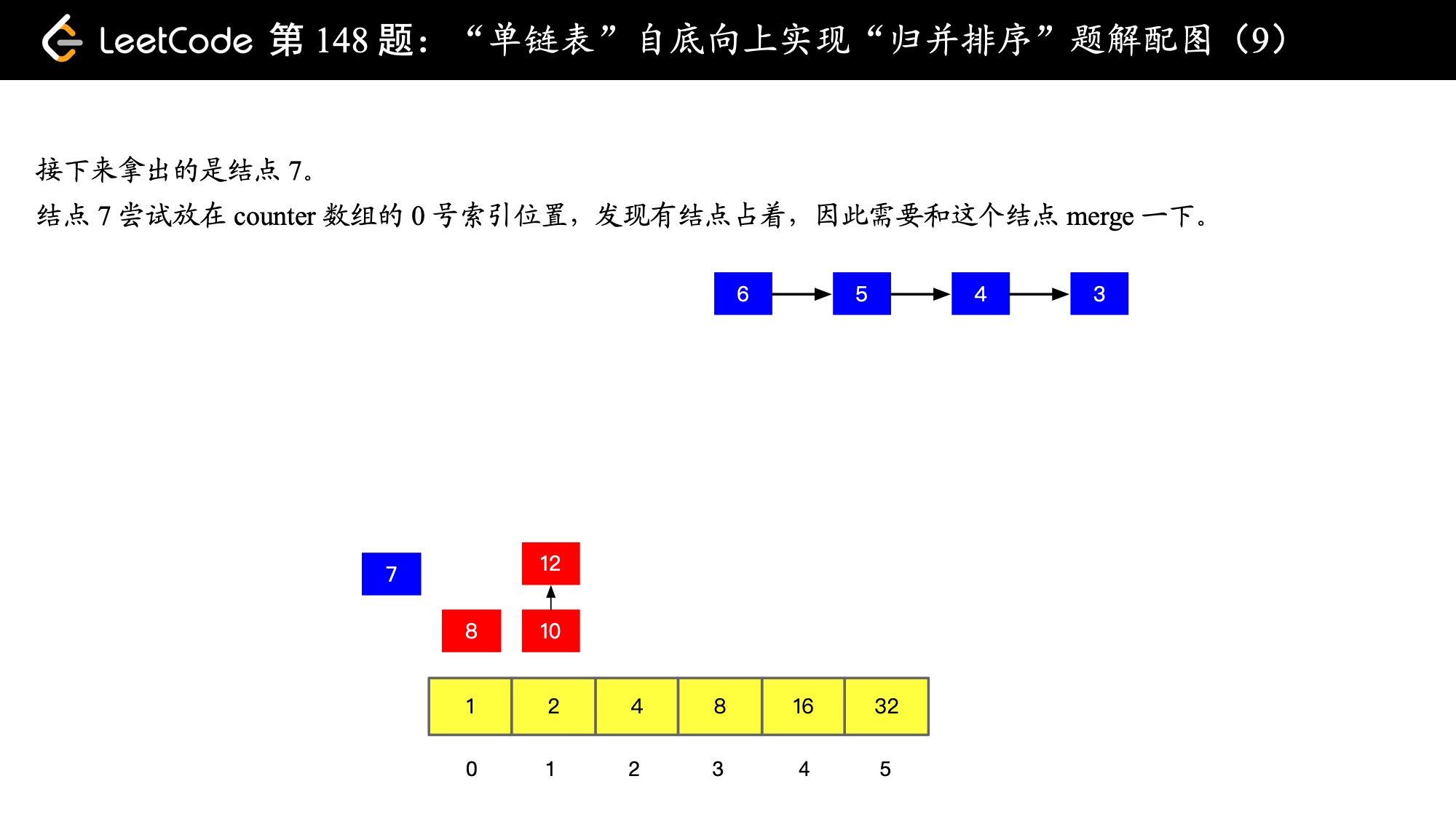 ),
),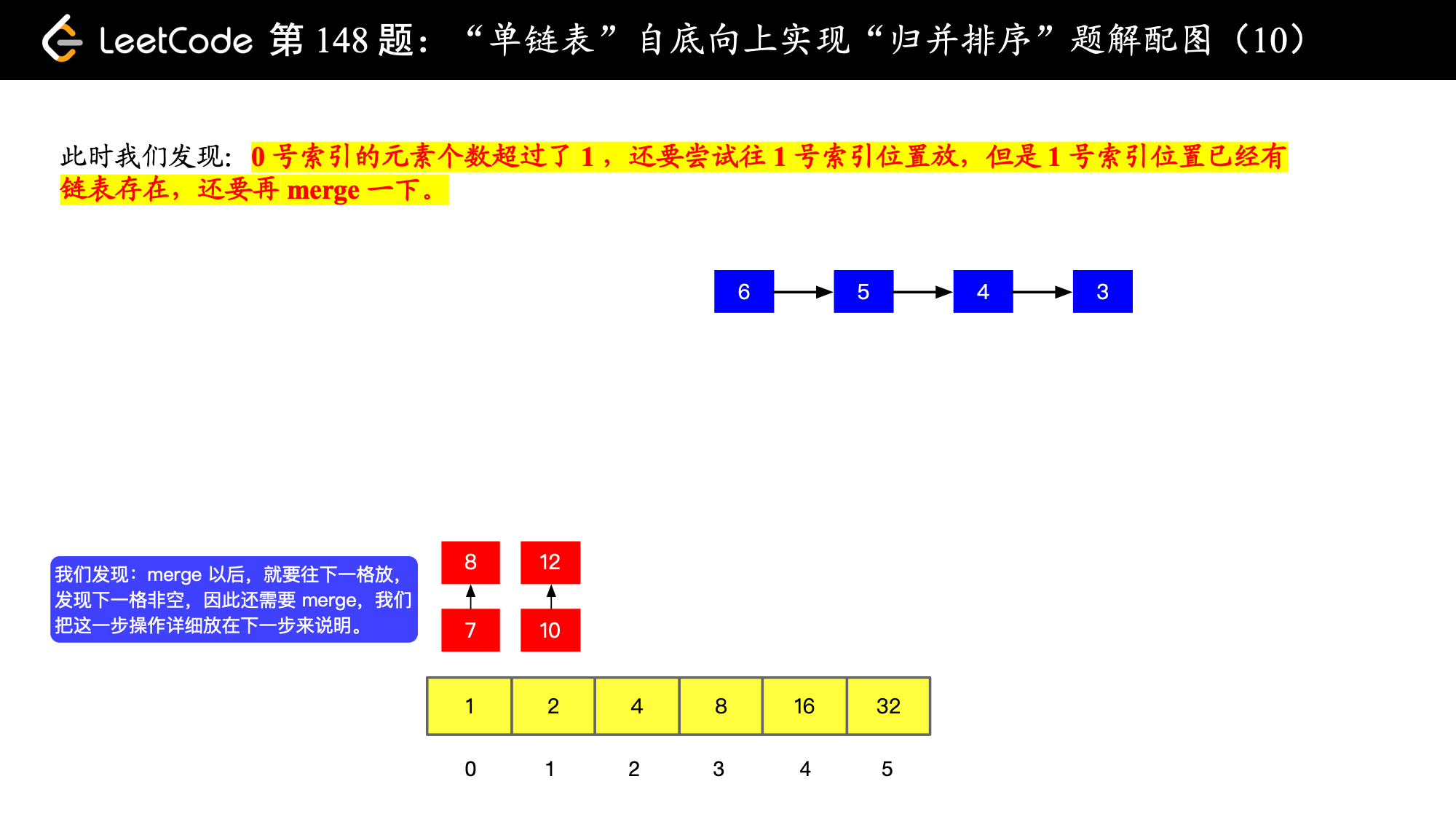 ),
),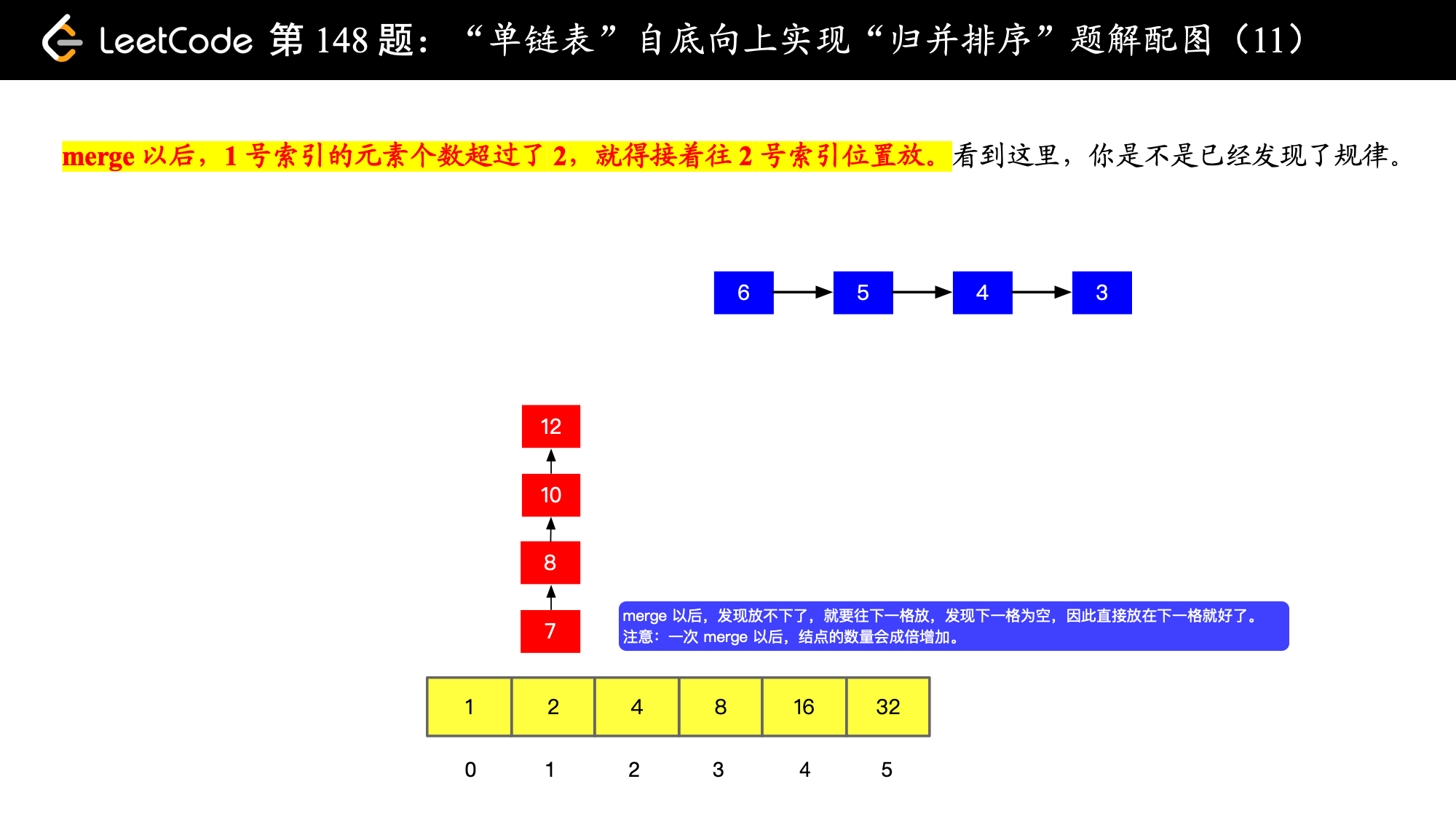 ),
),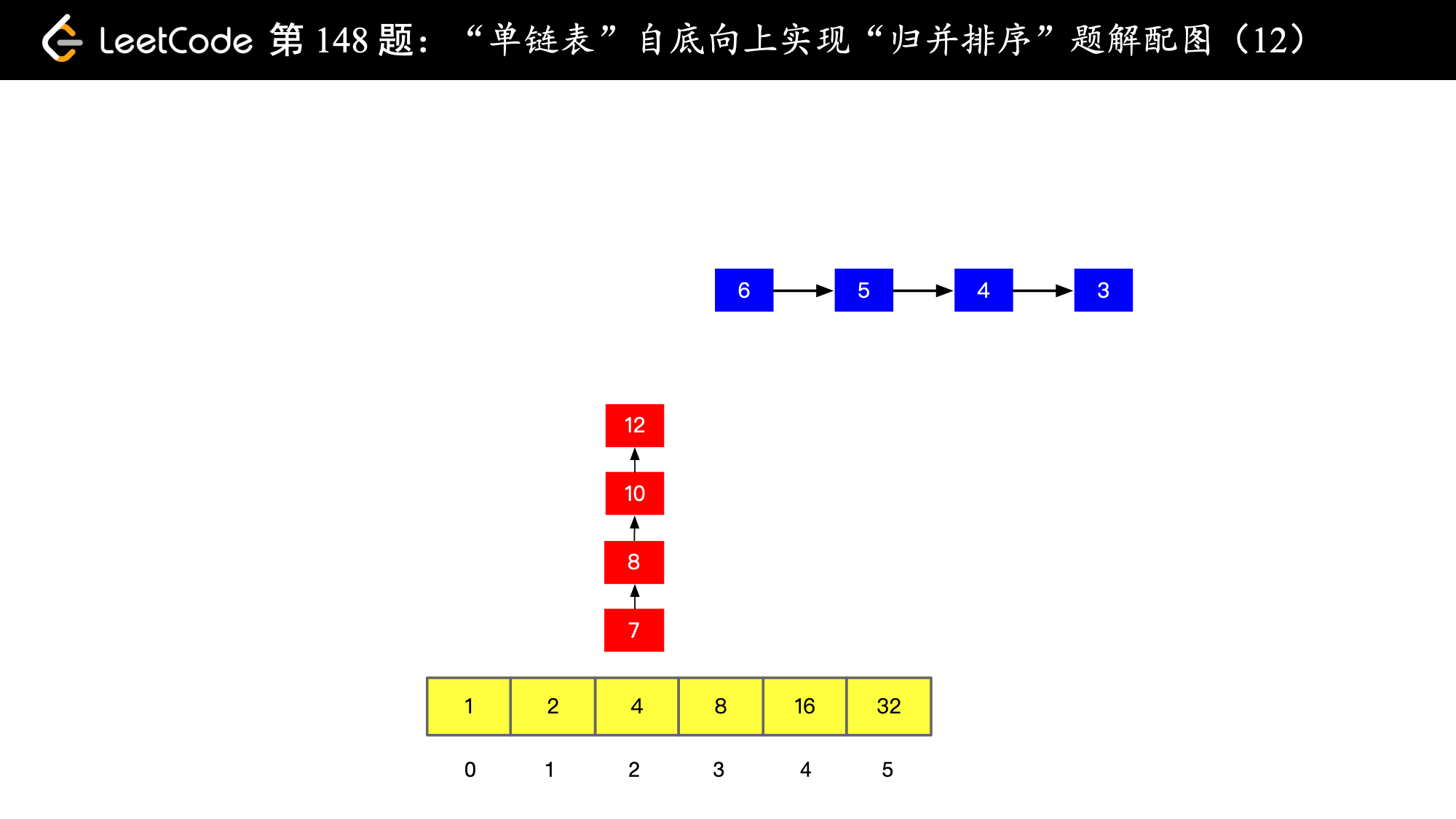 ),
),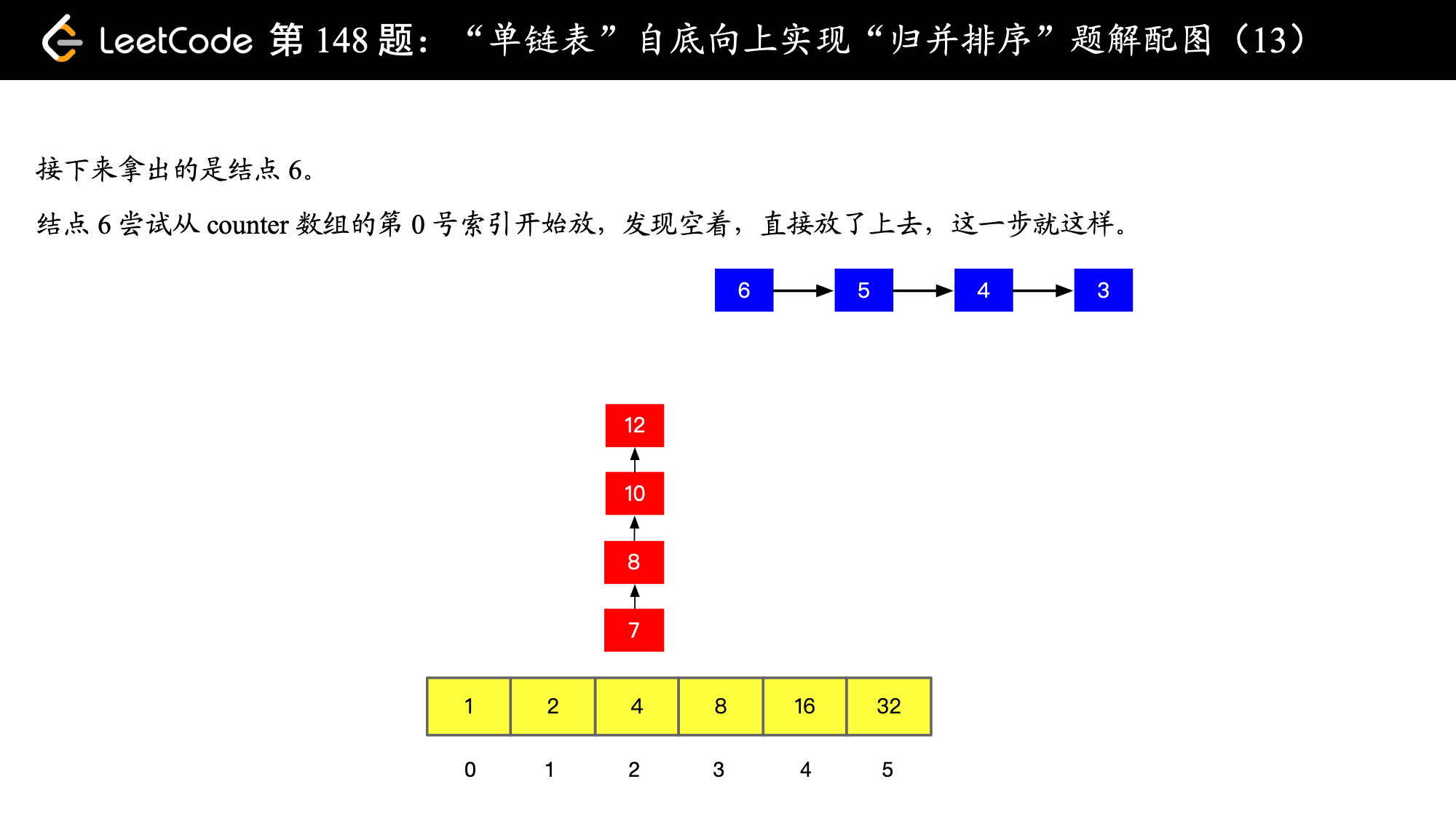 ),
),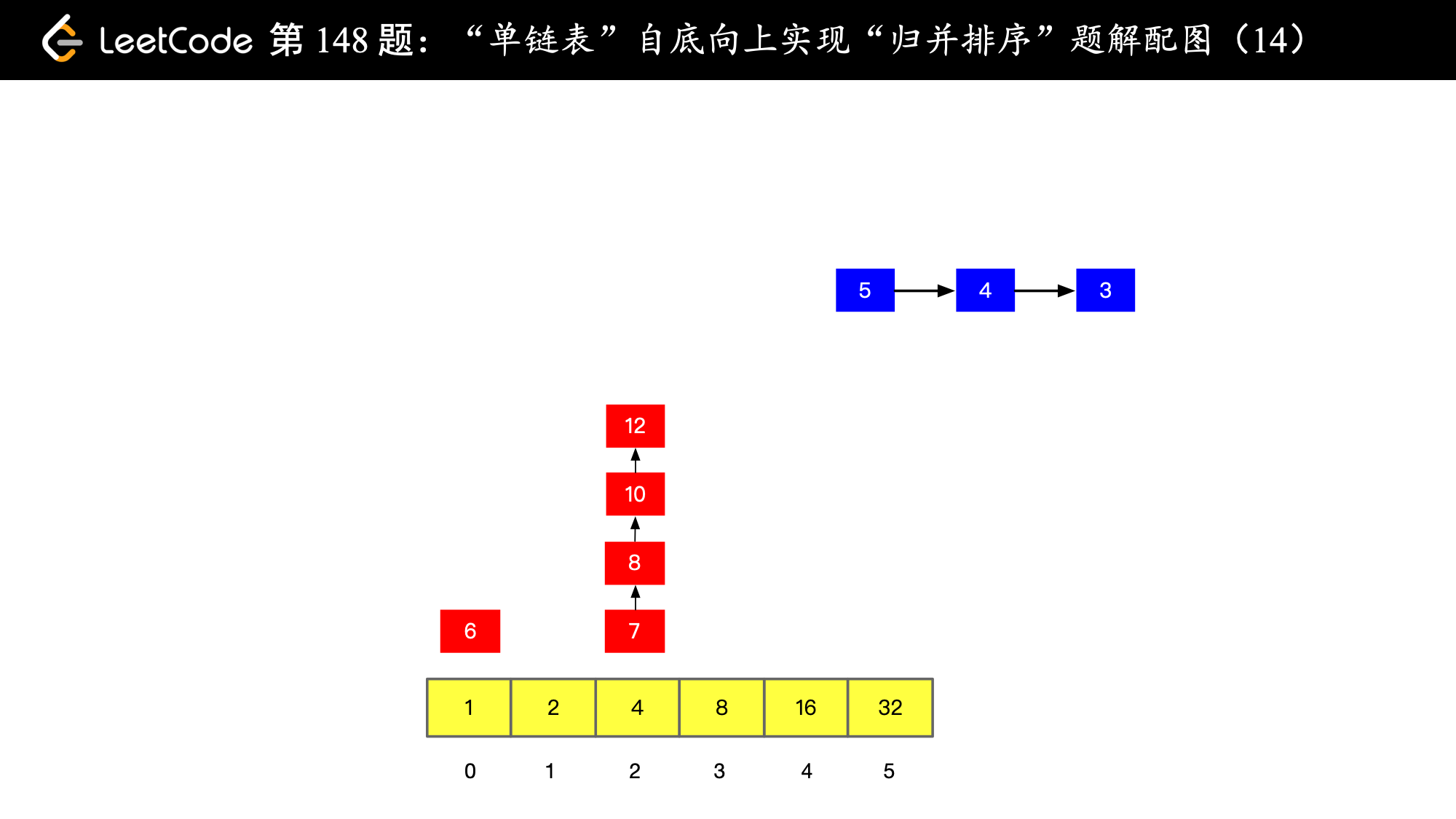 ),
),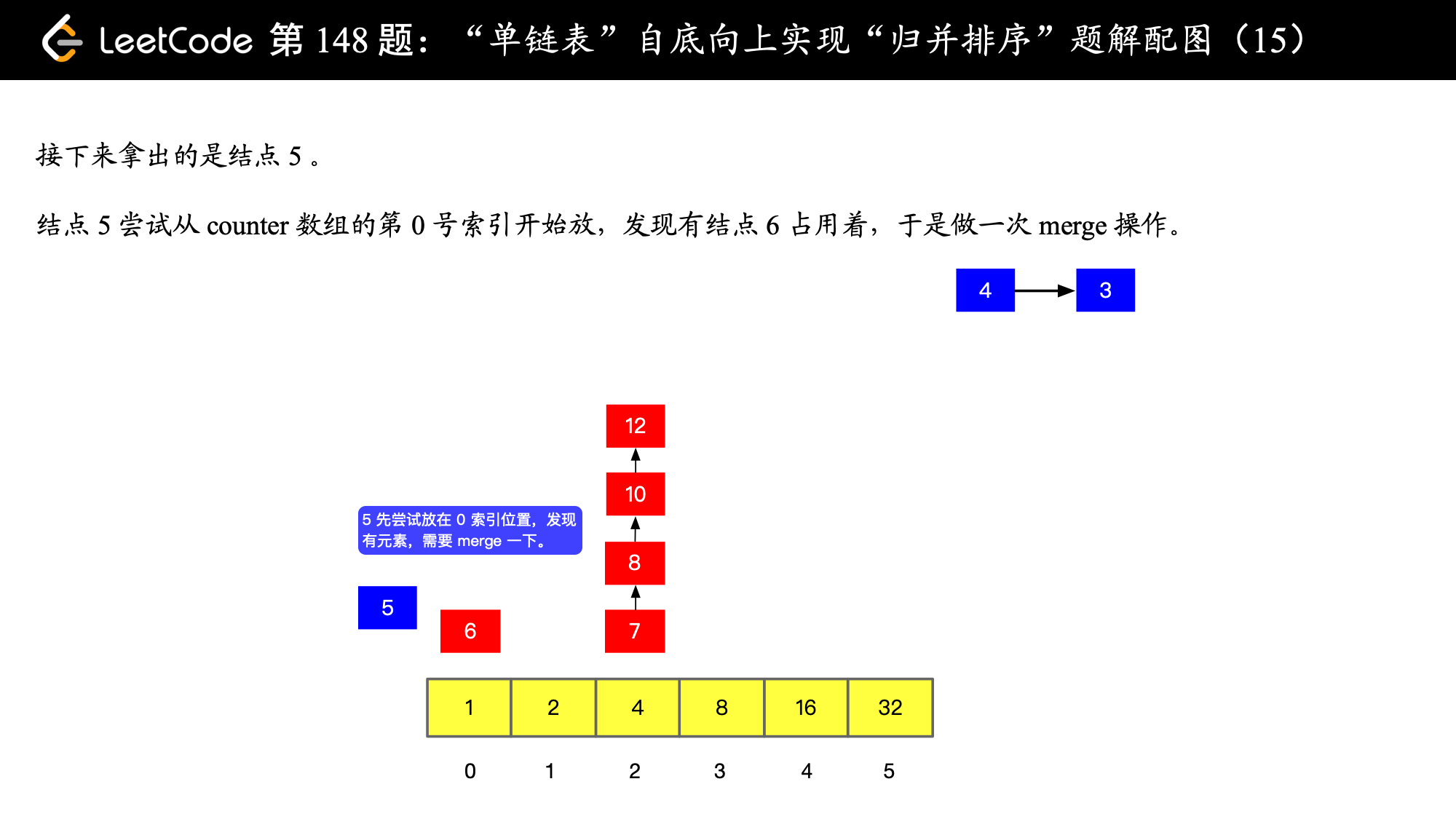 ),
),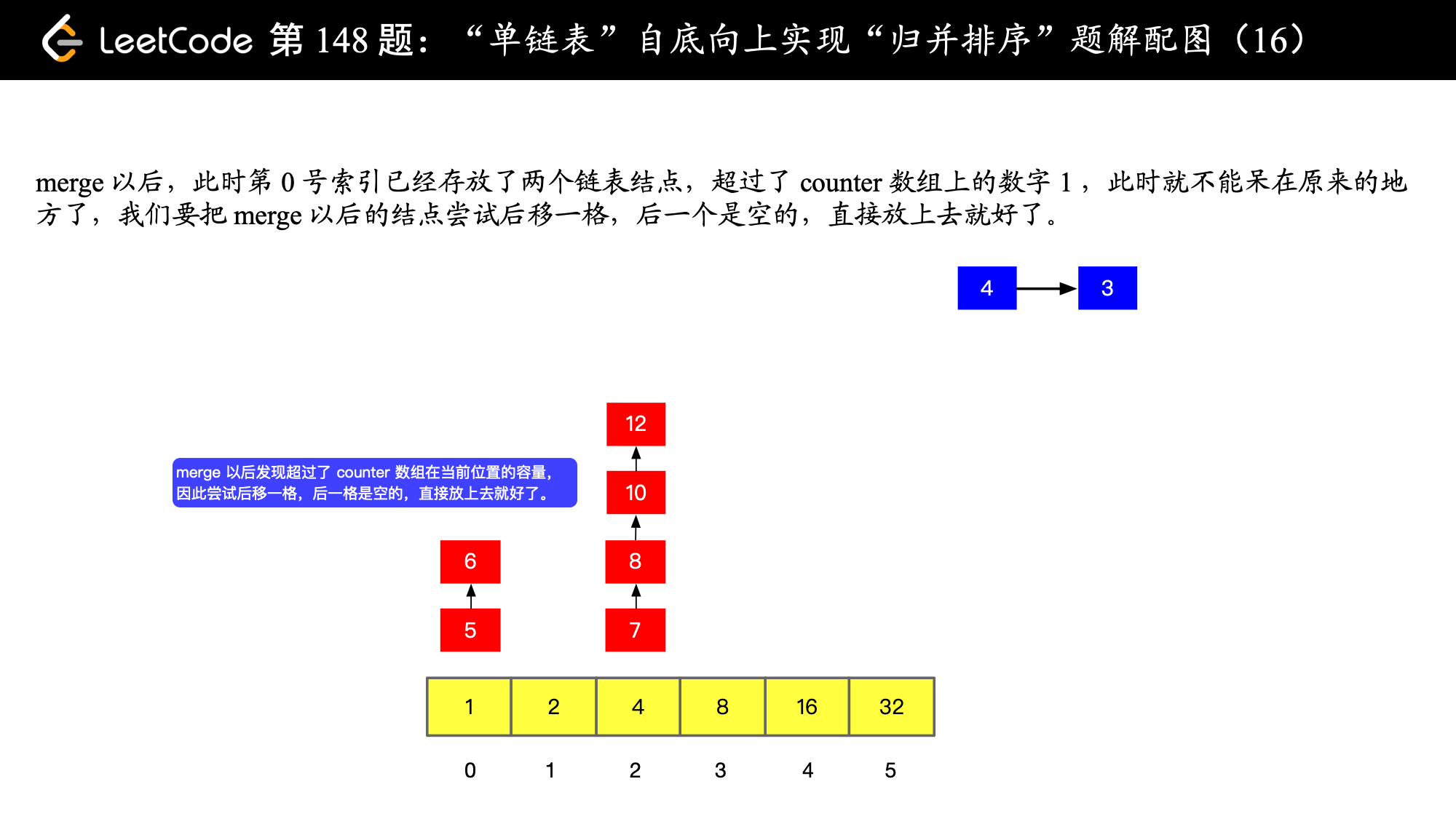 ),
), ),
), ),
), ),
), ),
),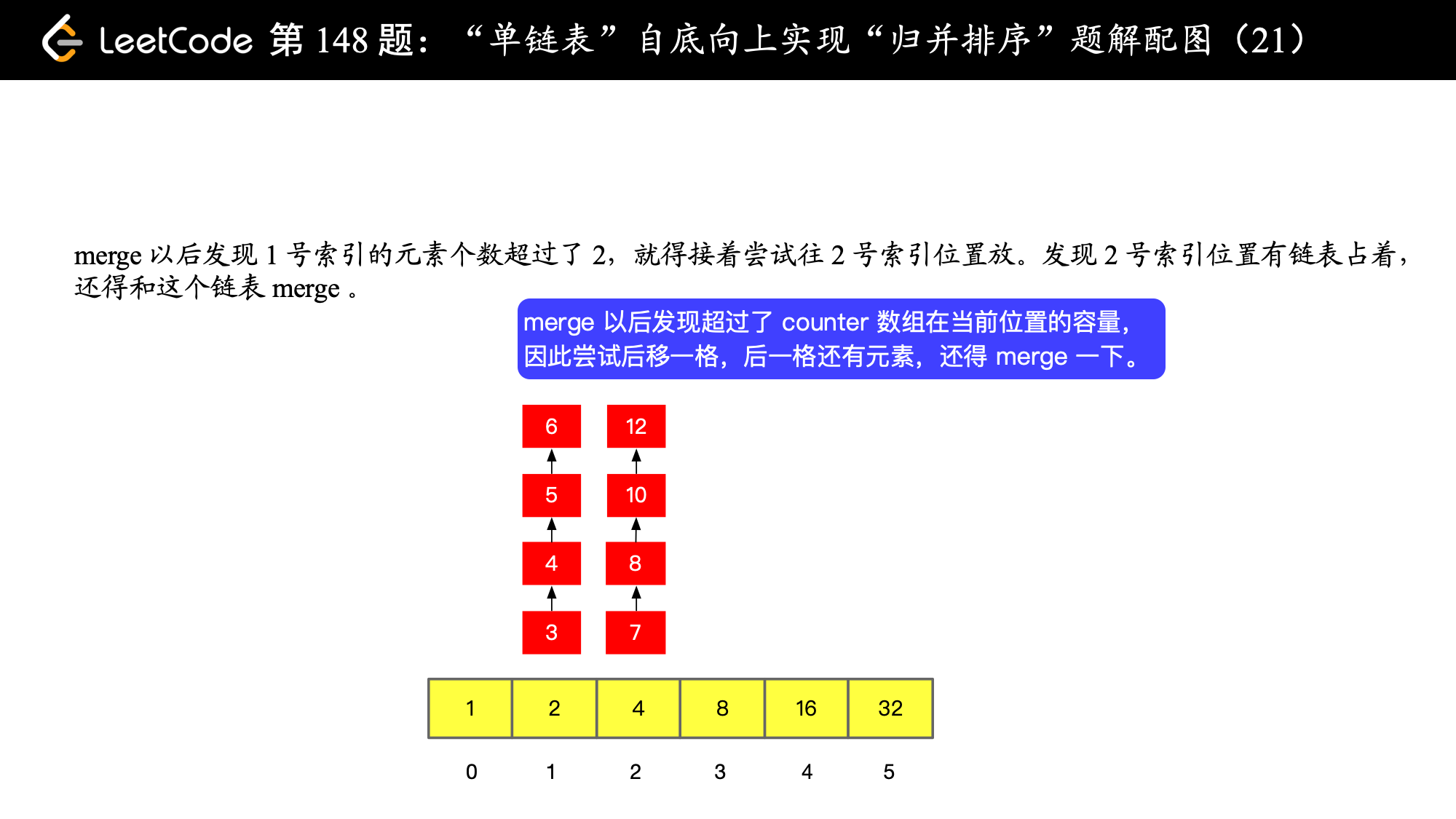 ),
),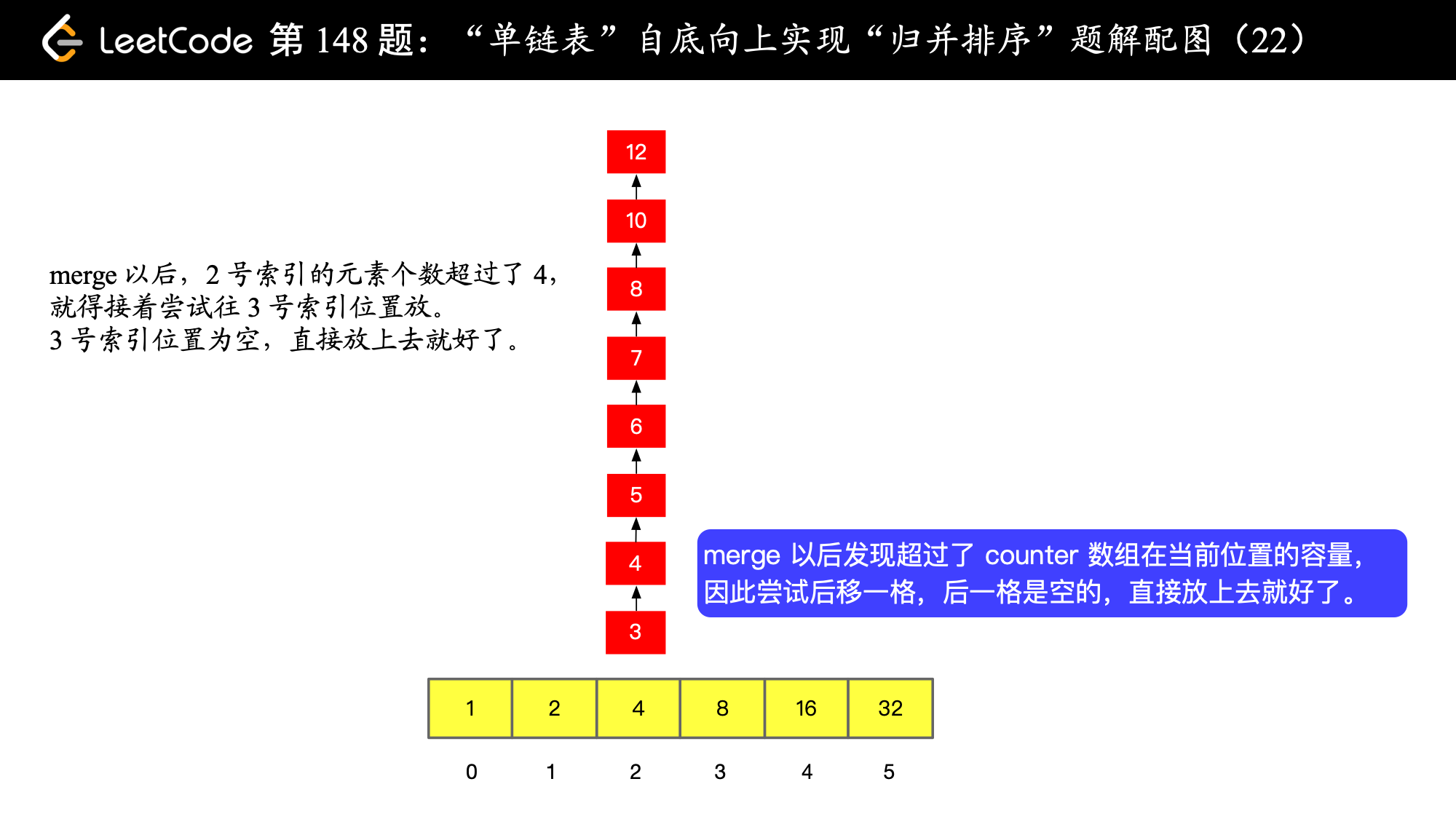 ),
),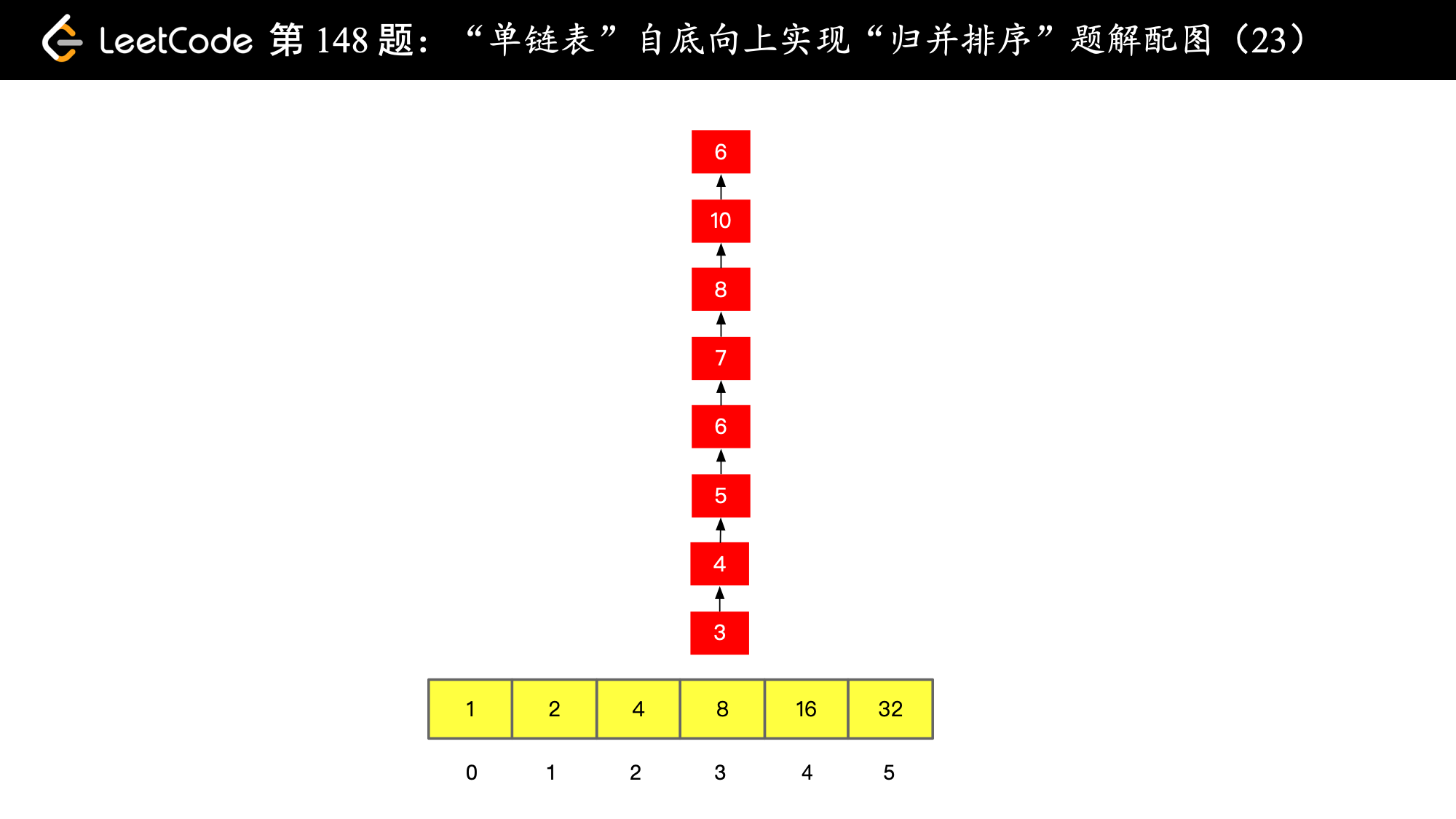 ),
),
参考代码:
Java 代码:
/**
* 自下而上进行归并
*
* @author liwei
*/
public class Solution2 {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
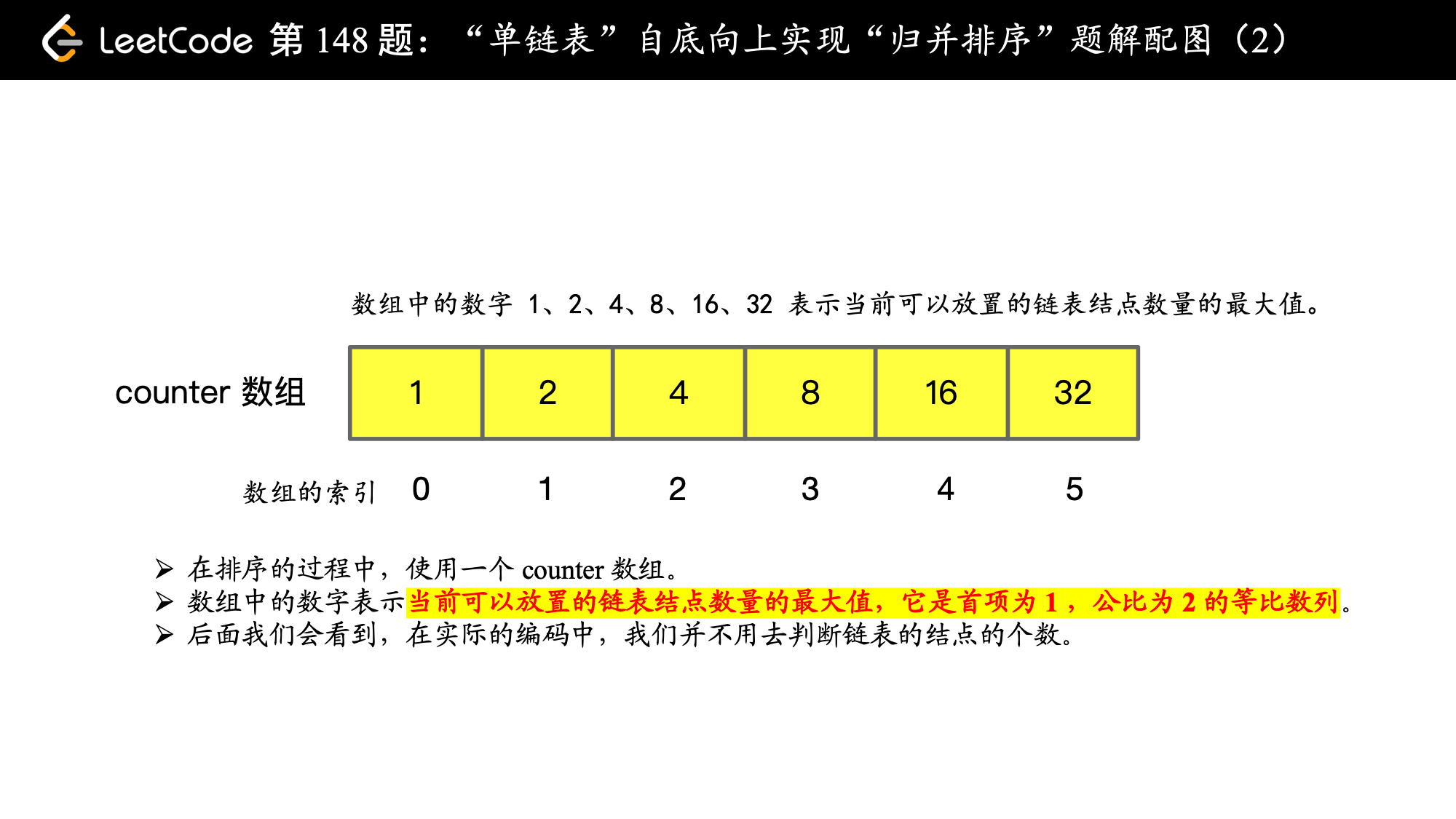
// 这里设置 64 ,是一个绰绰有余的数字,可以满足结点数量为 2^64 这么多的单链表的排序
ListNode[] counter = new ListNode[64];
ListNode curNode = head;
// 遍历到的最大的 counter 数组的索引
int maxIndex = 0;
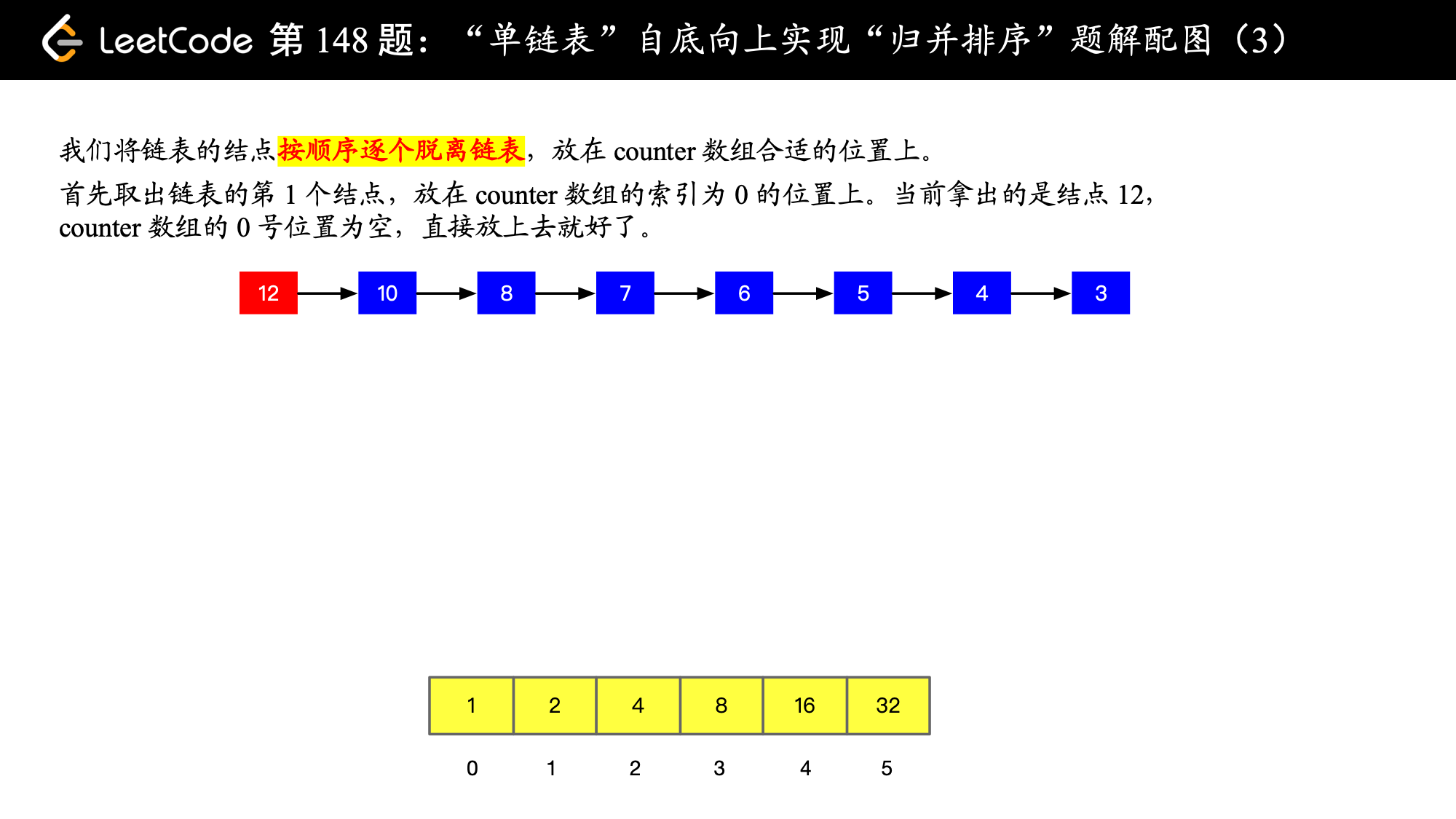
while (curNode != null) {
// 先把当前元素暂存起来,马上我们就要把它放到 counter 数组合适的位置上
ListNode carryNode = curNode;
// curNode 指针马上后移,方便下次处理
curNode = curNode.next;
// 拿出的节点就和原来的链表没有关系了,我们在 counter 数组中完成排序,所以要切断它和原链表的关系
carryNode.next = null;
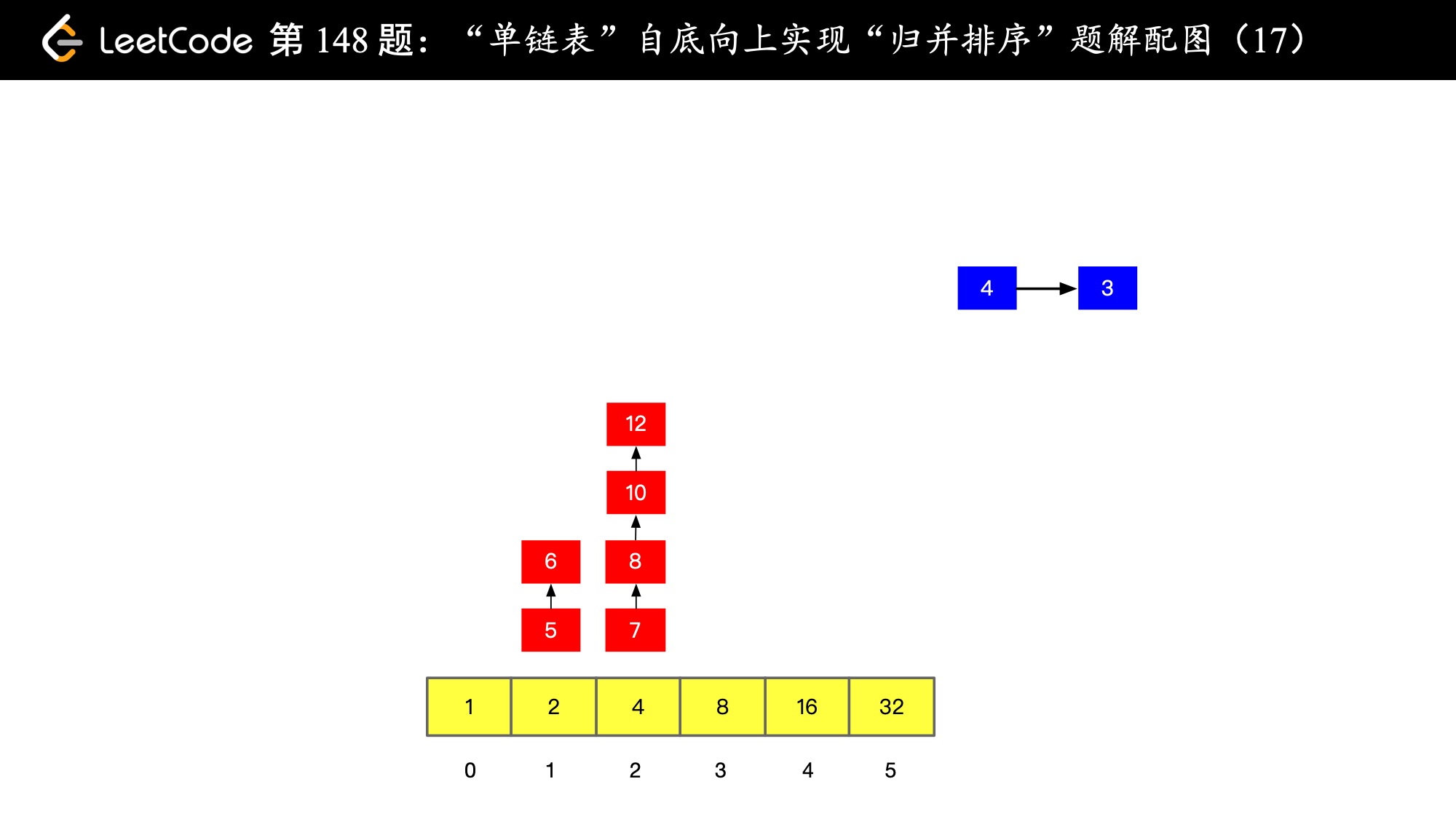
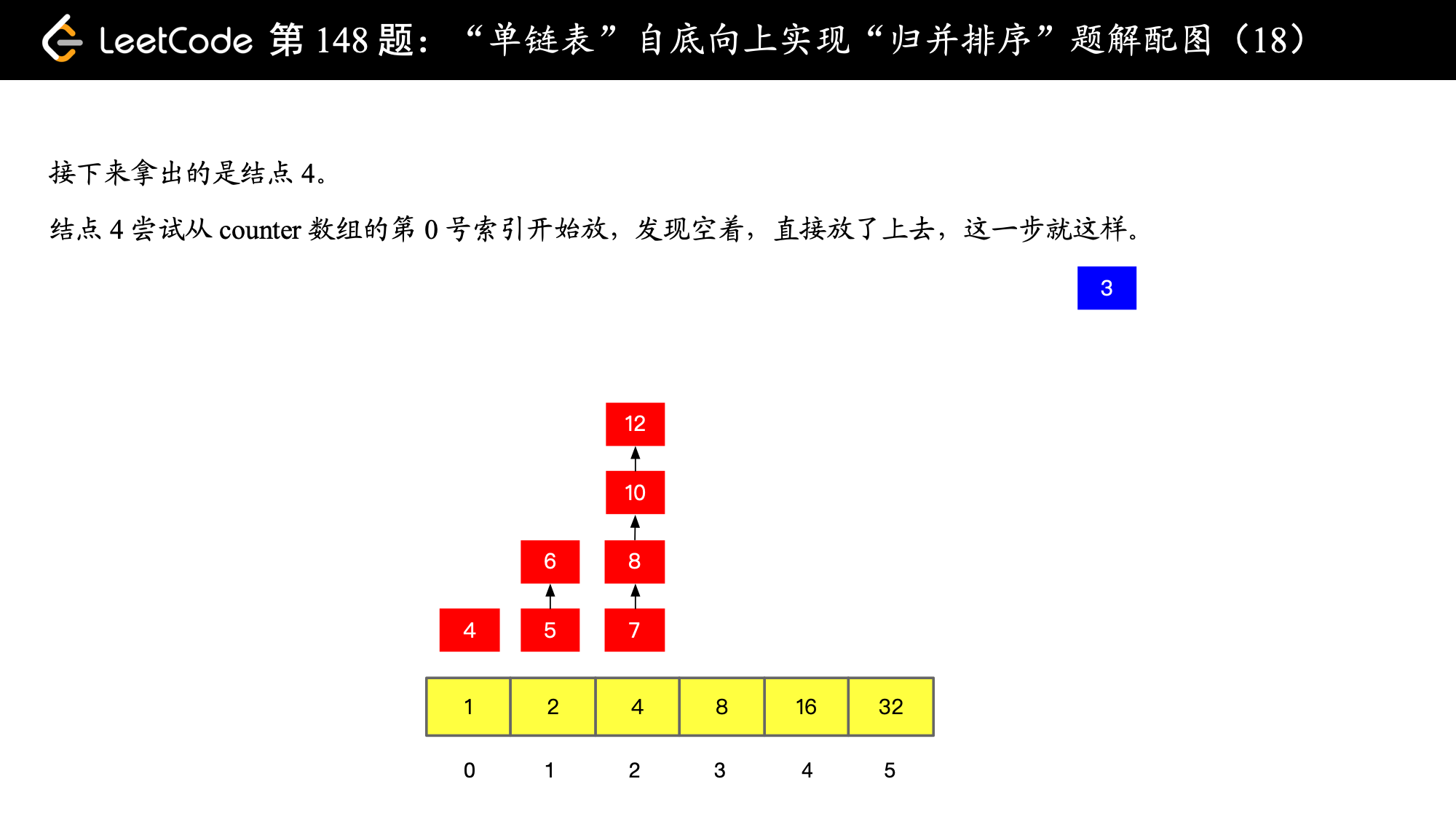
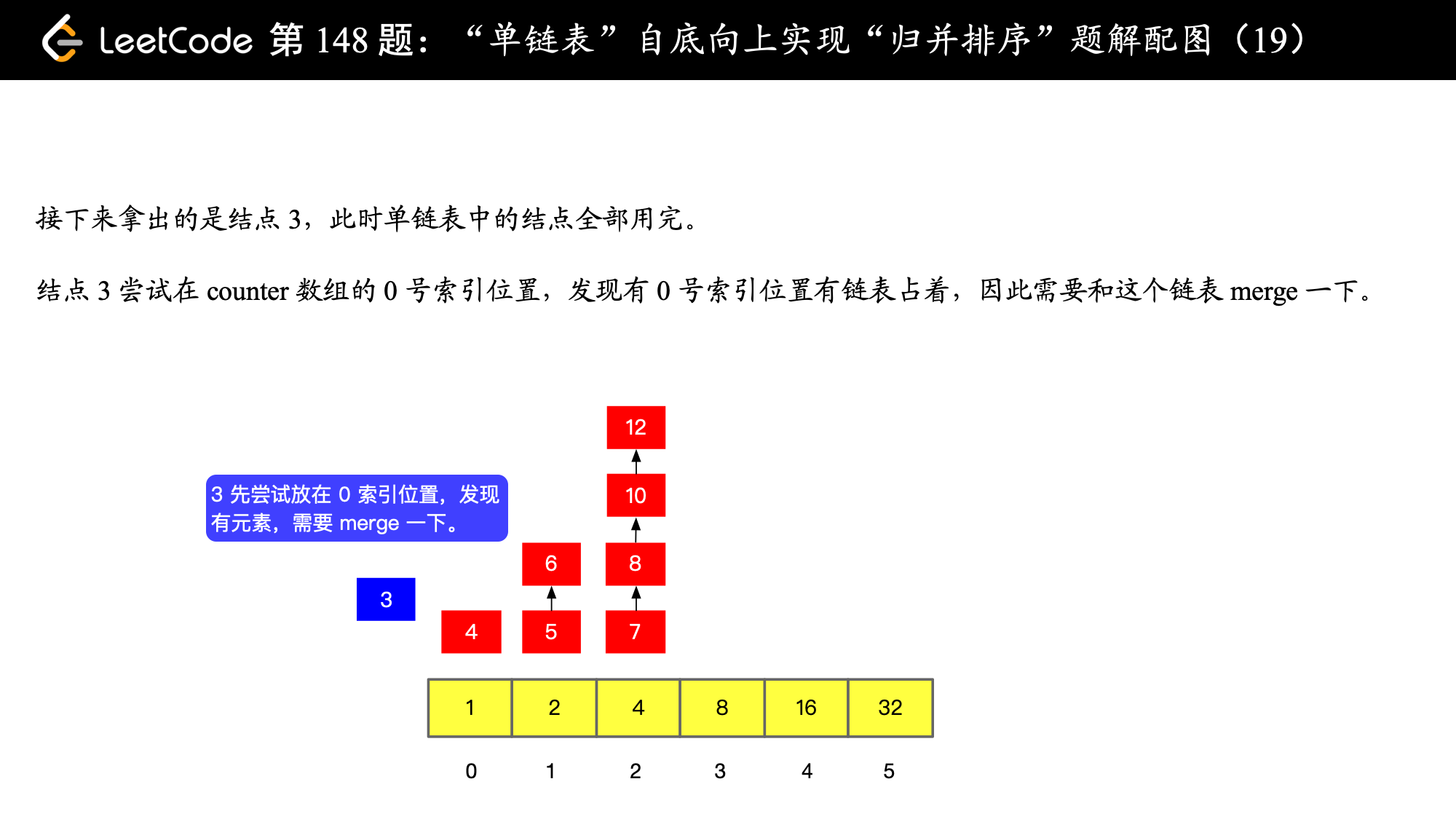
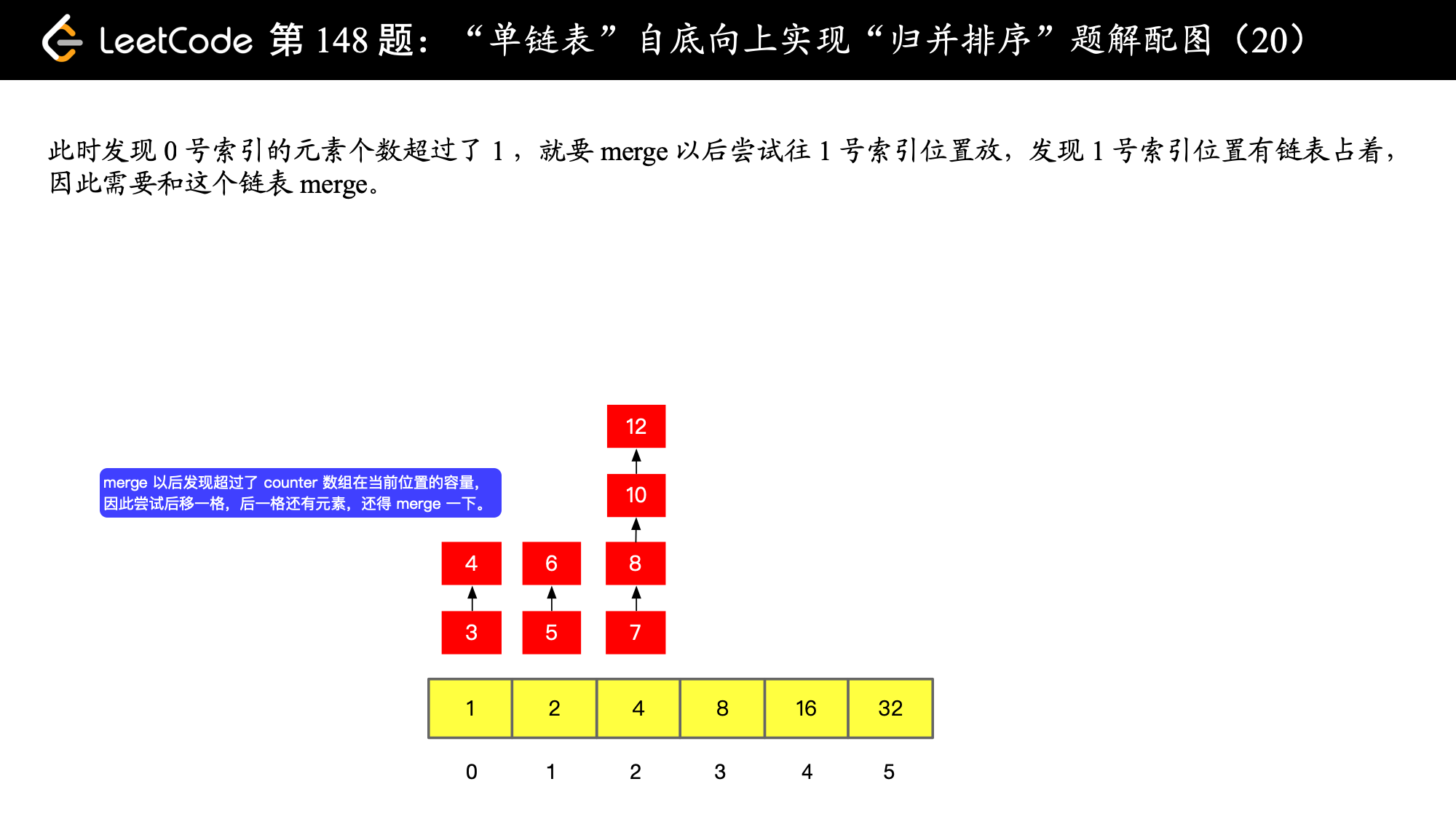
// 尝试从 counter 数组 0 号索引开始放置
int i = 0;
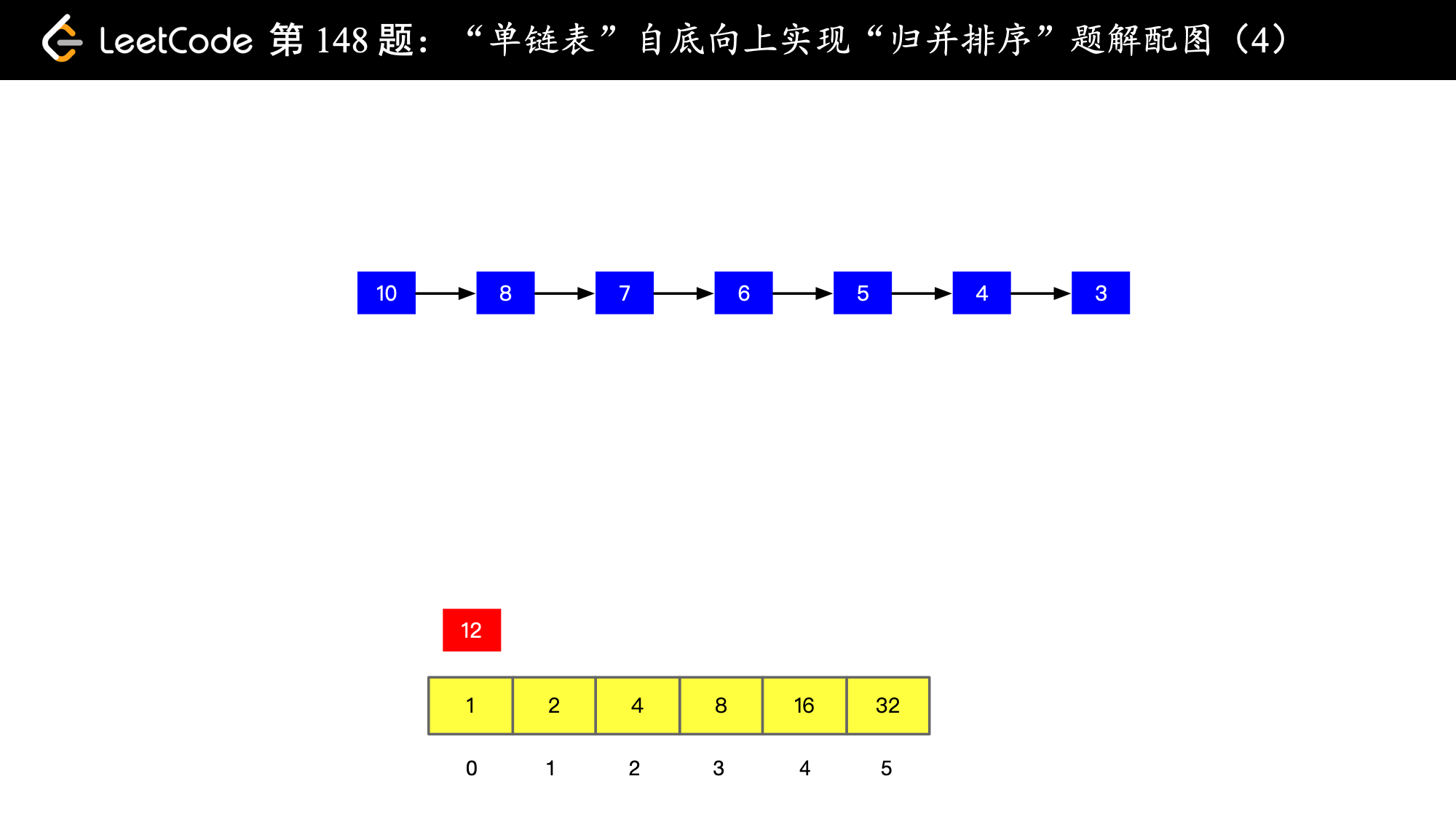
// 只要非空当前位置非空,就进行一次 merge,merge 以后尝试放到下一格,如果下一格非空就继续合并
// 合并以后再尝试放到下一格,直到下一格为空,直接放在那个为空的下一格就好
while (counter[i] != null) {
ListNode newMergeNode = mergeOfTwoSortedListNode(carryNode, counter[i]);
counter[i] = null;
i++;
carryNode = newMergeNode;
}
// 遇到了空,就把 carryNode 放在数组的这个位置上
counter[i] = carryNode;
// 记录最多使用到 counter 数组的第几位,最后合并的时候要用上
if (i > maxIndex) {
maxIndex = i;
}
}
// 遍历整个 count 数组,将它们全部归并,这个操作就和归并 n 个有序单链表是一样的了,我们这里采用两两归并
// 还可以采用 LeetCode 第 23 题的办法完成这一步
// 参考:https://liweiwei1419.github.io/leetcode-solution/leetcode-0023-merge-k-sorted-lists/
ListNode res = null;
for (int i = 0; i <= maxIndex; i++) {
if (counter[i] != null) {
res = mergeOfTwoSortedListNode(res, counter[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
/**
* 归并两个已经排好序的单链表,是我们非常熟悉的操作了,可以递归完成,也可以穿针引线,这里我们递归完成
*
* @param l1 顺序存放的单链表1
* @param l2 顺序存放的单链表2
* @return 合并以后的单链表
*/
private ListNode mergeOfTwoSortedListNode(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeOfTwoSortedListNode(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeOfTwoSortedListNode(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = new int[]{9, 8, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 1};
ListNode head = new ListNode(nums);
Solution2 solution2 = new Solution2();
ListNode sortList = solution2.sortList(head);
System.out.println(sortList);
}
}下面补充“自顶向下”的“归并排序”的写法,注意 3 种写法的不同之处。
Python 代码 1:
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# 找到中点
slow = head
fast = head
# 使用这种方式,当结点个数为 2 个时候,slow 在左结点
# 不会导致死循环
while fast.next and fast.next.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
head2 = slow.next
slow.next = None
lnode = self.sortList(head)
rnode = self.sortList(head2)
return self.__merge_two_sorted_list(lnode, rnode)
def __merge_two_sorted_list(self, head1, head2):
if head1 is None:
return head2
if head2 is None:
return head1
if head1.val < head2.val:
head1.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1.next, head2)
return head1
else:
head2.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1, head2.next)
return head2Python 代码 2:
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
# 这里有个小陷阱,如果遇到问题,不要着急,代码调试就好了
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# 找到中点
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
# 这里要保存一下前一个指针
p = slow
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
p.next = None
# print_node_list(head)
# print_node_list(head2)
lnode = self.sortList(head)
rnode = self.sortList(slow)
return self.__merge_two_sorted_list(lnode, rnode)
def __merge_two_sorted_list(self, head1, head2):
if head1 is None:
return head2
if head2 is None:
return head1
if head1.val < head2.val:
head1.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1.next, head2)
return head1
else:
head2.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1, head2.next)
return head2
def create_node_list(arr):
head = ListNode(arr[0])
cur = head
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
cur.next = ListNode(arr[i])
cur = cur.next
return head
def print_node_list(head):
while head:
print(head.val, '->', end=' ')
head = head.next
print('NULL')
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [4, 2, 1, 3]
head = create_node_list(arr)
print_node_list(head)
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortList(head)
print_node_list(result)Python 代码 3:
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
# 这里有个小陷阱,如果遇到问题,不要着急,代码调试就好了
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# 玄机在这里,如果非要用 while fast and fast.next:
# 让快指针先走一步,以避免死循环
slow = head
fast = head.next
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
new_head = slow.next
slow.next = None
lnode = self.sortList(head)
rnode = self.sortList(new_head)
return self.__merge_two_sorted_list(lnode, rnode)
def __merge_two_sorted_list(self, head1, head2):
if head1 is None:
return head2
if head2 is None:
return head1
if head1.val < head2.val:
head1.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1.next, head2)
return head1
else:
head2.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1, head2.next)
return head2
def create_node_list(arr):
head = ListNode(arr[0])
cur = head
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
cur.next = ListNode(arr[i])
cur = cur.next
return head
def print_node_list(head):
while head:
print(head.val, '->', end=' ')
head = head.next
print('NULL')
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [4, 2, 1, 3]
head = create_node_list(arr)
print_node_list(head)
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortList(head)
print_node_list(result)class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
ListNode(int[] nums) {
ListNode currNode = this;
currNode.val = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
currNode.next = new ListNode(nums[i]);
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
ListNode currNode = this;
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
while (currNode != null) {
s.append(currNode.val);
s.append(" -> ");
currNode = currNode.next;
}
s.append("NULL");
return s.toString();
}
}伪代码
current = dummy.next;
tail = dummy;
for (step = 1; step < length; step *= 2) {
while (current) {
// left->@->@->@->@->@->@->null
left = current;
// left->@->@->null right->@->@->@->@->null
right = cut(current, step); // 将 current 切掉前 step 个头切下来。
// left->@->@->null right->@->@->null current->@->@->null
current = cut(right, step); // 将 right 切掉前 step 个头切下来。
// dummy.next -> @->@->@->@->null,最后一个节点是 tail,始终记录
// ^
// tail
tail.next = merge(left, right);
while (tail->next) tail = tail->next; // 保持 tail 为尾部
}
}作者:ivan_allen
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/solution/148-pai-xu-lian-biao-bottom-to-up-o1-kong-jian-by-/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
好了,下面是比较正式的代码。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode dummyHead(0);
dummyHead.next = head;
auto p = head;
int length = 0;
while (p) {
++length;
p = p->next;
}
for (int size = 1; size < length; size <<= 1) {
auto cur = dummyHead.next;
auto tail = &dummyHead;
while (cur) {
auto left = cur;
auto right = cut(left, size); // left->@->@ right->@->@->@...
cur = cut(right, size); // left->@->@ right->@->@ cur->@->...
tail->next = merge(left, right);
while (tail->next) {
tail = tail->next;
}
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
ListNode* cut(ListNode* head, int n) {
auto p = head;
while (--n && p) {
p = p->next;
}
if (!p) return nullptr;
auto next = p->next;
p->next = nullptr;
return next;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode dummyHead(0);
auto p = &dummyHead;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
p->next = l1;
p = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
p->next = l2;
p = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
p->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return dummyHead.next;
}
};作者:ivan_allen
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/solution/148-pai-xu-lian-biao-bottom-to-up-o1-kong-jian-by-/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
练习3:LeetCode 第 148 题:单链表的排序,使用归并排序
传送门:英文网址:148. Sort List ,中文网址:148. 排序链表 。
在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
示例 1:
输入: 4->2->1->3 输出: 1->2->3->4示例 2:
输入: -1->5->3->4->0 输出: -1->0->3->4->5
写一个排序算法,用 $O(n\log n)$ 的时间复杂度为一个链表进行排序。
对于单链表而言,归并排序是一个不错的选择。
思路1:自顶向下的归并排序。
注意1:特别注意下面这么一段:
while fast.next and fast.next.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next说明:
- 这个方法走到这里,因为有前面的特判,所以至少得有 $2$ 个结点,才可以排序。而取中点的操作,只有在“下个结点”和“下下结点”都存在的时候,才能这么做;
- 看看这个循环的循环体就明白了。
注意2:找到中间结点以后,记得把链表“从中切断”,这是符合逻辑的。
Python 代码:
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# 找到中点
slow = head
fast = head
while fast.next and fast.next.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
head2 = slow.next
slow.next = None
lnode = self.sortList(head)
rnode = self.sortList(head2)
return self.__merge_two_sorted_list(lnode, rnode)
def __merge_two_sorted_list(self, head1, head2):
if head1 is None:
return head2
if head2 is None:
return head1
if head1.val < head2.val:
head1.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1.next, head2)
return head1
else:
head2.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1, head2.next)
return head2另一种写法:
特别注意,如果是
while fast and fast.next:
p = slow
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next这种取法,遇到两个结点的时候,slow 会向前走一步,但是截断得在 slow 结点之前,否则会进入死循环,按照我说的,画一个两个结点的链表就很清楚了。
遇到死循环的时候,不要着急,还有耐心 debug,分析代码运行流程,很多时候问题就迎刃而解了。
Python 代码:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
# 这里有个小陷阱,如果遇到问题,不要着急,代码调试就好了
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# 找到中点
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
p = slow
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
p.next = None
# print_node_list(head)
# print_node_list(head2)
lnode = self.sortList(head)
rnode = self.sortList(slow)
return self.__merge_two_sorted_list(lnode, rnode)
def __merge_two_sorted_list(self, head1, head2):
if head1 is None:
return head2
if head2 is None:
return head1
if head1.val < head2.val:
head1.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1.next, head2)
return head1
else:
head2.next = self.__merge_two_sorted_list(head1, head2.next)
return head2
def create_node_list(arr):
head = ListNode(arr[0])
cur = head
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
cur.next = ListNode(arr[i])
cur = cur.next
return head
def print_node_list(head):
while head:
print(head.val, '->', end=' ')
head = head.next
print('NULL')
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [4, 2, 1, 3]
head = create_node_list(arr)
print_node_list(head)
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortList(head)
print_node_list(result)思路2:自底向上的归并排序。
我以前写了一个示意图,可以点这里看,思想还是很简单的。
(本节完)



